Results:
– Fibroblasts from patients with Alzheimer’s disease all show moderate and significant radiosensitivity associated with a defect in recognizing and repairing DNA double-strand breaks via delayed transit of the ATM protein to the cell nucleus.
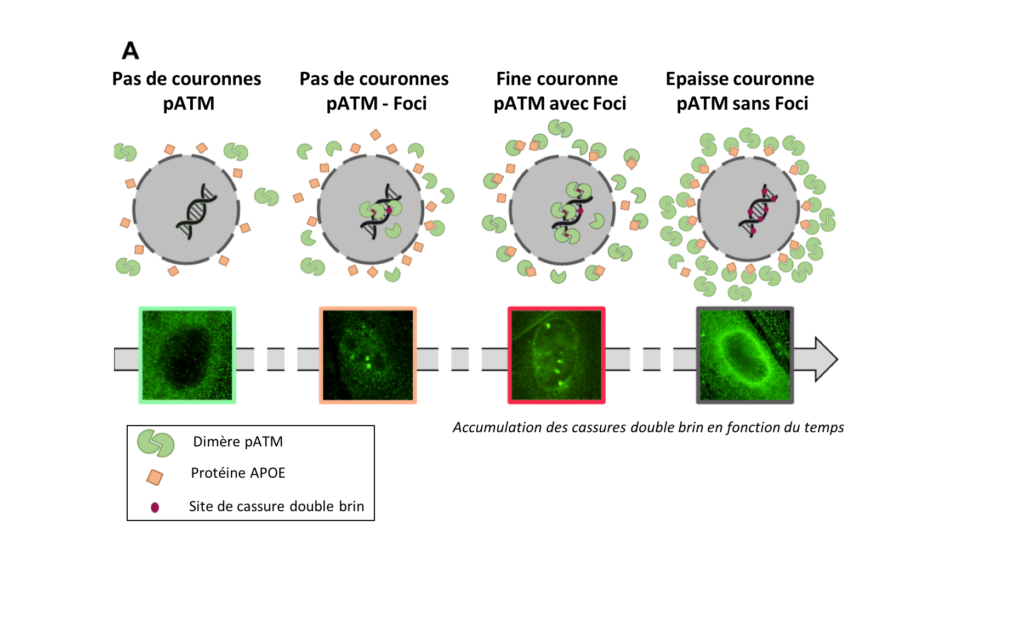
– Alzheimer’s fibroblasts spontaneously display a specific abnormal perinuclear localization of the ATM protein, forming a “perinuclear crown” suggesting its aggregation around the cell nucleus.
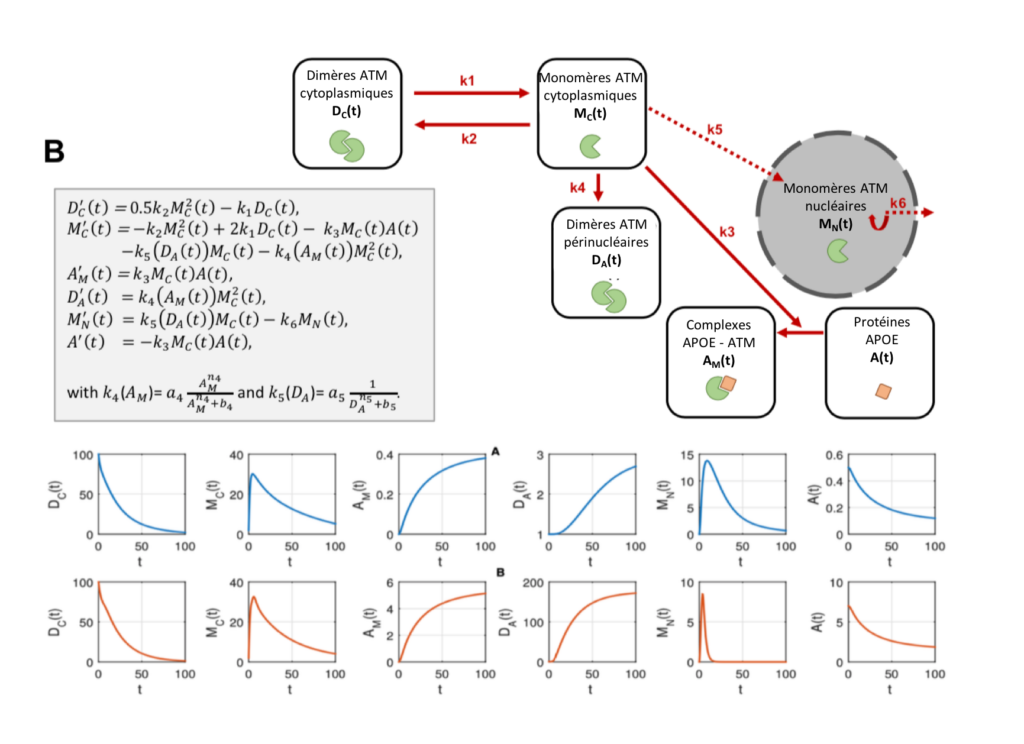
– Alzheimer’s fibroblasts display a specific protein partnership between the ATM and APOE proteins (the APOE gene is known to be involved in the onset and rapid progression of the disease).
Discussion:
Perinuclear localization of the ATM protein was significantly observed in all the Alzheimer’s disease fibroblast cell lines in our study. It was therefore hypothesized that these perinuclear crowns could serve as a specific biomarker of Alzheimer’s disease, useful for its detection, progression and/or potential treatment. This model has been consolidated by a new mathematical approach and has been patented along with other specific biomarkers by the Neolys Diagnostics team.
Mechanistic model of perinuclear crown formation of pATM protein in fibroblasts from patients with Alzheimer’s disease.